"Abortions Unplugged:All You Need to Know!"
I had to take a break from writing because I was preparing for and writing an exam, which caused a delay. Now that my exam is over, I’m back and ready to continue from where I left off.

In our previous discussion, we said we will talk more on why a pregnant woman may need an abortion and how to perform a safe abortion and further expatiate complications and the management options available for abortion so here we go.
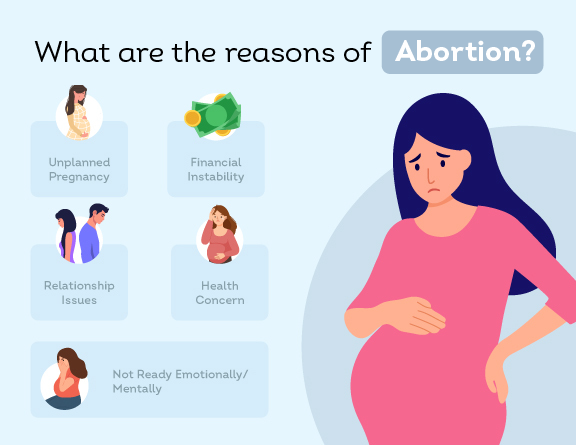
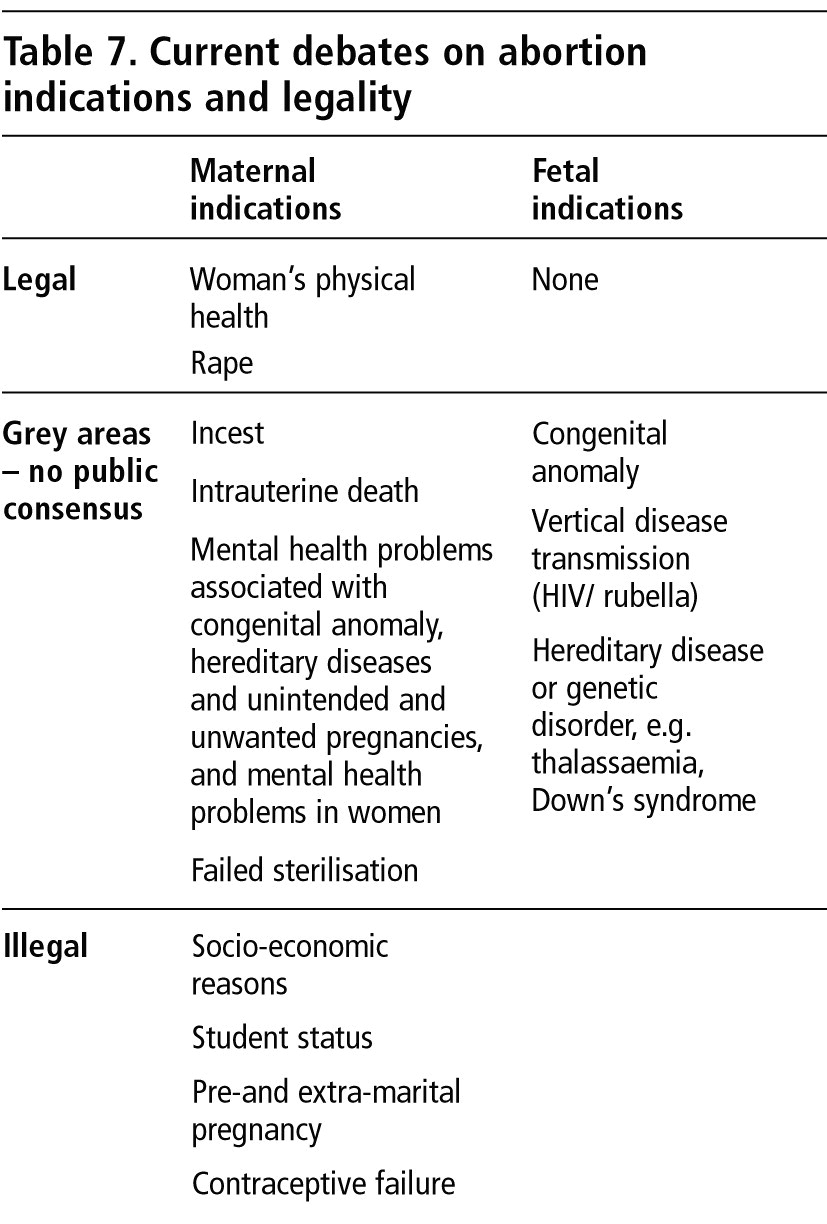
Indications for Abortion
Abortion may be considered for various reasons, including maternal health risks, fetal anomalies, and socio-economic factors. Medical conditions such as preeclampsia, severe cardiac disease, and malignancies may necessitate termination to preserve maternal health. Additionally, severe congenital anomalies incompatible with life, such as anencephaly, may warrant abortion.
Having explored the reasons a woman may require an abortion, we now turn our attention to the methods available to ensure a safe and effective procedure.

Safe Abortion Methods
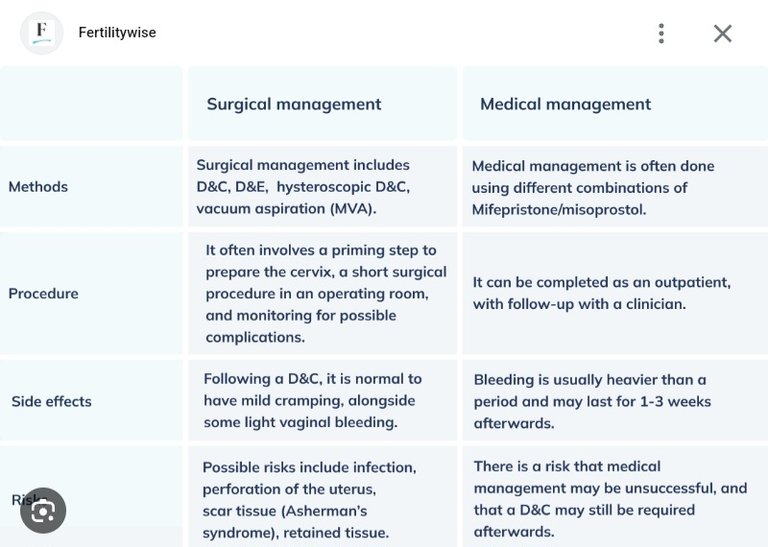
Safe abortion methods depend on gestational age and available medical resources. They can be classified as medical abortion and surgical abortion:
- Medical Abortion (Up to 9–12 weeks)
Uses a combination of mifepristone and misoprostol to induce abortion.
An alternative regimen includes misoprostol alone when mifepristone is unavailable. The process mimics a miscarriage and is considered safe when supervised.
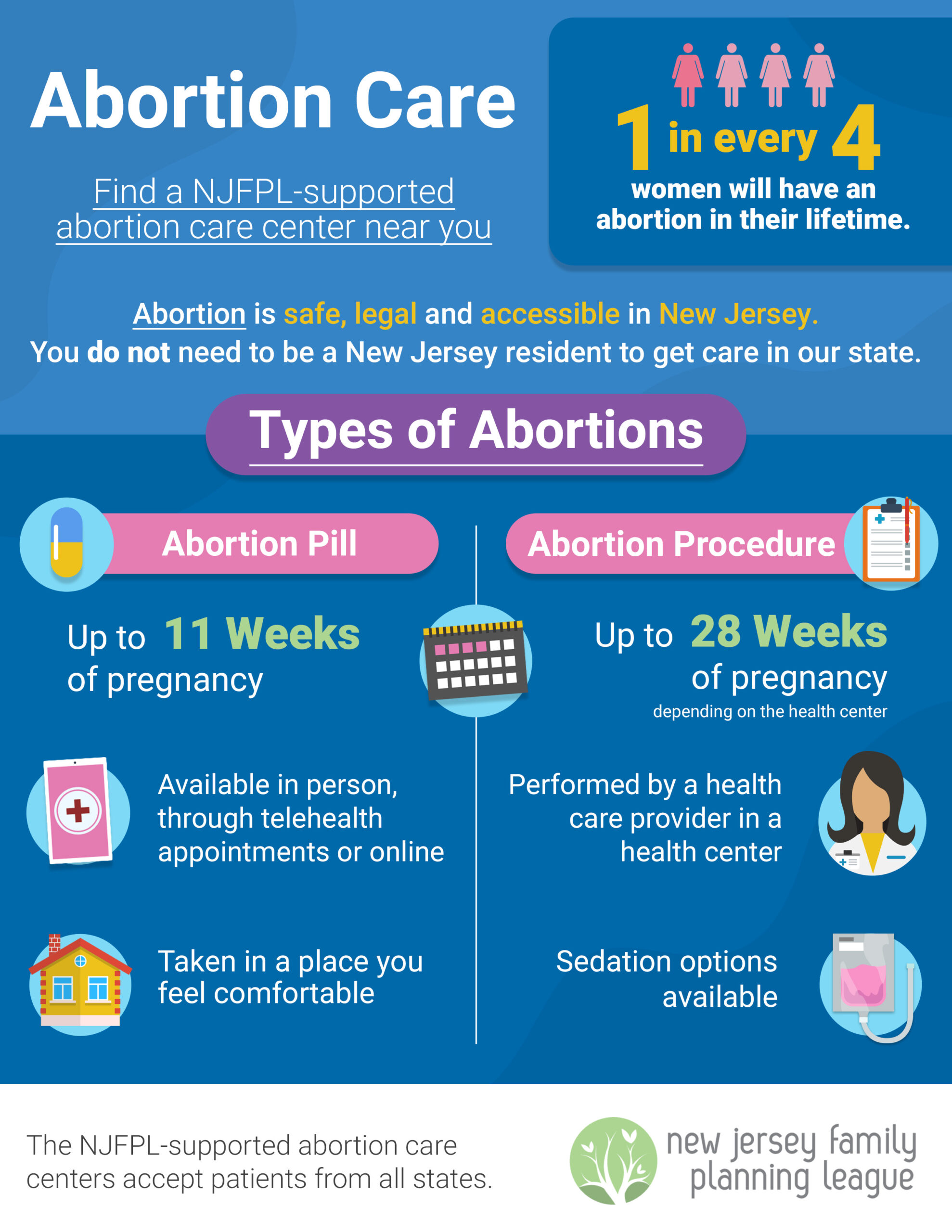

- Surgical Abortion
Manual Vacuum Aspiration (MVA) (Up to 12–14 weeks): Uses suction to remove uterine contents.
Dilation and Evacuation (D&E) (After 14 weeks): Involves cervical dilation followed by forceps removal of fetal tissue.
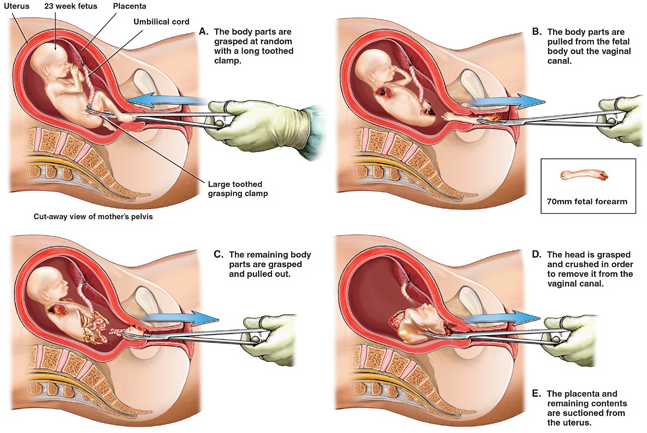
Induction Abortion (Late second trimester): High-dose misoprostol or oxytocin induces labor for expulsion.
Both methods require proper provider training and sterile conditions to minimize risks. Despite the safety of these procedures, complications can still arise, requiring prompt recognition and management.
Complications of Abortion and Their Management
Complications can be categorized into immediate and delayed:
Immediate Complications
Hemorrhage: Can occur due to uterine atony, cervical laceration, or retained products.
Management: Uterine massage, oxytocics (e.g., oxytocin, misoprostol), surgical intervention if severe.
Infection (Septic Abortion): Fever, pelvic pain, foul-smelling discharge.
Management: IV antibiotics, evacuation of retained products if needed.
Uterine Perforation: More common with surgical abortions.
Management: Expectant if minor, laparoscopic repair if severe.Delayed Complications
Asherman Syndrome: Intrauterine adhesions from excessive curettage.
Future Pregnancy Complications: Increased risk of preterm birth or placental abnormalities.
By understanding these risks, healthcare providers can implement strategies to ensure safe abortion care while minimizing complications.
Sources of my pictures
1.https://www.pacehospital.com/mtp-medical-abortion
2.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1016/S0968-8080%2804%2924018-6
3.https://njfpl.org/abortion-care-infographic/
4.https://www.prolifeproducts.org/dilation-and-evacuation-abortion-diagram
5.https://apnews.com/article/abortion-covid-science-health-2d52ebf9efc6ef06f03e788fecd13013
- https://www.fertilitywise.com/research/complete-guide-to-dilation-and-curettage-d-c .Had all the help from AI, CHATGPT.

Congratulations @rkm1okpoti! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 100 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPThis is quite an interesting read. In my opinion, I'd say that abortion should be legalize in all aspects. Basically, that will save alot of young lives from quack doctors.
It really really will
Thank you
You are welcome 🤗