🐧#ViernesDeEscritorio. Automatizando la actualización de Linux Mint con scripts.💻ESP/EN

Captura de pantalla.

Automatizando la actualización de Linux Mint con scripts | Automating Linux Mint upgrade with scripts |
|---|---|
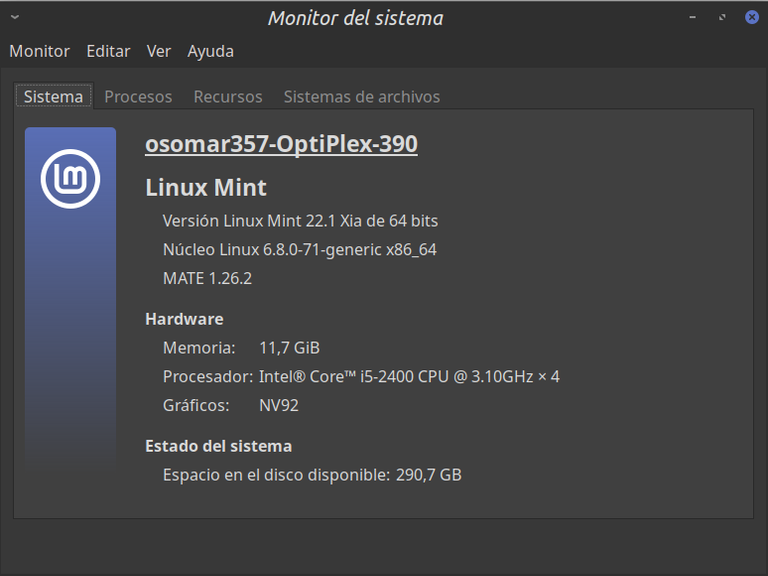
Saludos, comunidad, mis mejores deseos para todos. Como todos mis lectores saben, soy usuario de Linux Mint y de Debian, pero ahora estoy usando Linux Mint 22.1 Xia, de 64 Bits, con escritorio Mate 1.26.2, que es un escritorio que me gusta mucho y me trae grandes recuerdos de cuando inicié en Linux en el año 2000. Yo siempre recomiendo Linux Mint para las personas que están migrando de Windows a Linux, y eso se debe a que es un sistema muy estable, muy amigable y de fácil uso. Pero también tiene herramientas como los “scripts de Bash” que nos permiten profundizar más en la experiencia de ser usuarios de Linux, y nos permiten automatizar ciertas tareas que nos permiten ahorrar tiempo, evitar errores y hacer que el sistema trabaje por nosotros. La idea de este artículo es explicar qué es un script, qué es Bash, cómo funciona y dejar un script, bien explicado y automatizado, de modo que el usuario y el lector de este post lo pueda adaptar a sus necesidades. | Greetings, community, my best wishes to all. As all my readers know, I am a Linux Mint and Debian user, but now I am using Linux Mint 22.1 Xia, 64-bit, with Mate desktop 1.26.2, which is a desktop that I really like and brings back great memories of when I started on Linux in 2000. I always recommend Linux Mint for people who are migrating from Windows to Linux, and that's because it's a very stable, very friendly and easy-to-use system. But it also has tools such as “Bash scripts" that allow us to delve deeper into the experience of being Linux users, and allow us to automate certain tasks that allow us to save time, avoid errors and make the system work for us. The idea of this article is to explain what a script is, what Bash is, how it works and leave a script, well explained and automated, so that the user and the reader of this post can adapt it to their needs. |
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
¿Qué es un script y qué es Bash? | What is a script and what is Bash? |
|---|---|
Un script es un conjunto de comandos utilizados para realizar tareas en un lenguaje de programación. En nuestro caso, lo podemos definir de manera mucho más sencilla: “como un archivo de texto, donde colocamos los comandos que normalmente colocamos manualmente en la terminal, con la intención de que se realicen de manera automática”. (Definición personal) El lenguaje más común para realizar los scripts es el Bash, que significa: Bourne Again Shell, que es el intérprete de comandos predeterminado en casi todas las distribuciones de Linux. | A script is a set of commands used to perform tasks in a programming language. In our case, we can define it much more simply: "as a text file, where we place the commands that we normally place manually in the terminal, with the intention that they are performed automatically”. (Personal definition) The most common scripting language is Bash, which stands for: Bourne Again Shell, which is the default command interpreter in almost all Linux distributions. |

La ventaja y las razones para usar los scripts: | The advantage and reasons for using scripts: |
|---|---|
|
|

¿Cómo se crean los scripts? | How are the scripts created? |
|---|---|
|
|

Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
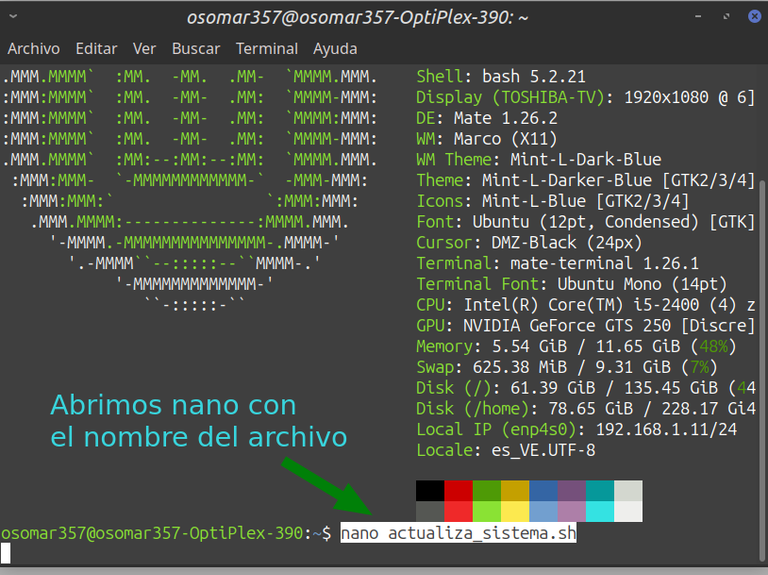
2- Vamos a abrir nano para hacer un script que llamaremos: actualiza_sistema.sh. | 2- Let's open nano to make a script that we will call: actualiza_sistema.sh . |
|---|---|
|
|
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
| |
|---|---|
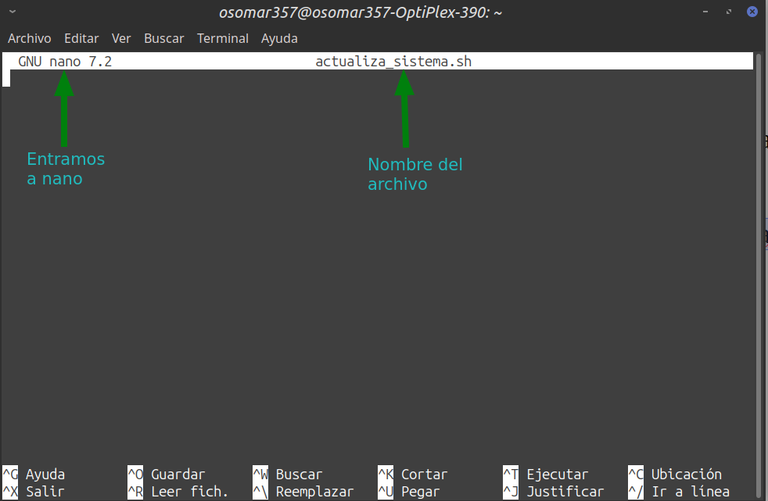
Donde sucede lo siguiente: a) nano: abre el editor de texto. b) actualiza_sistema.sh: es el nombre del archivo que se va a crear. c) Se coloca la terminación “.sh” en el nombre, para indicar que el archivo es un shell script. | Where the following happens: a) nano: opens the text editor. (b) actualiza_sistema.sh : is the name of the file to be created. c) The ending “.sh” is placed in the name, to indicate that the file is a shell script. |
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
|
|
|---|---|
Ahora explicaremos el contenido del script: a) Primero vamos a colocar en nano: #!/bin/bash Esto indica que el archivo será ejecutado con Bash. Acá es importante informar que cuando uno coloca el signo (#) al comenzar una línea en un script, Bash toma esa línea como si fuese un comentario interno y por lo tanto no la ejecuta. b) echo "=== Iniciando actualización del sistema ≡" El comando “echo” muestra un comentario que se ve en la terminal cuando se ejecuta el script. Funciona así: “echo” es el comando que indica el comentario y lo que está entre las "…". Es el mensaje que se lee. c) El comando sudo apt update; se usa para descargar la lista de paquetes más recientes que esté disponible. d) El comando sudo apt upgrade -y se usa para instalar las actualizaciones, y la flag (-y) se usa para que se ejecute la aprobación de la instalación de manera automática, sin necesidad de que el usuario apruebe apretando la letra (s). e) El comando sudo apt autoremove -y: se usa para eliminar los paquetes que ya no son necesarios y las dependencias huérfanas. | Now we will explain the content of the script: a) First let's place in nano: #!/bin/bash This indicates that the file will be executed with Bash. Here it is important to inform that when one places the sign (#) at the beginning of a line in a script, Bash takes that line as if it were an internal comment and therefore does not execute it. b) echo "=== Starting system update ≡" The "echo" command displays a comment that is seen in the terminal when the script is executed. It works like this: "echo" is the command that indicates the comment and what is between the "...". This is the message that is being read. c) The sudo apt update command; it is used to download the most recent package list that is available. d) The sudo apt upgrade -y command is used to install the updates, and the flag (-y) is used to execute the approval of the installation automatically, without the need for the user to approve by pressing the letter (s). e) The sudo apt autoremove -y command: is used to remove packages that are no longer needed and orphaned dependencies. |
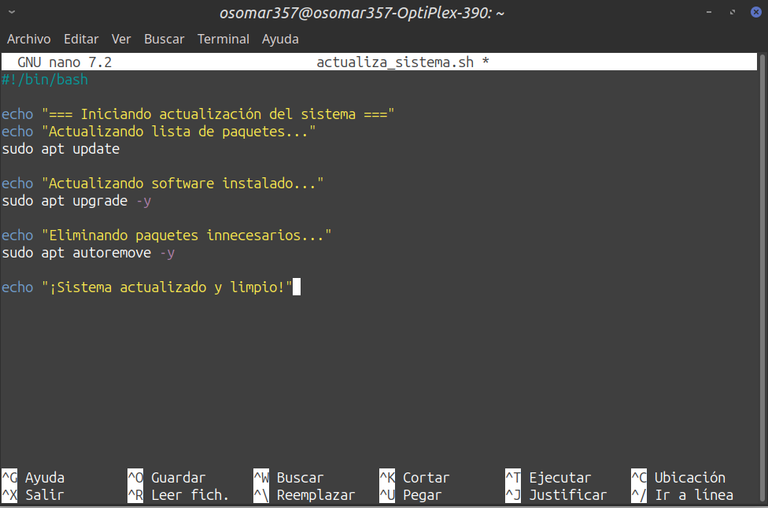
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Cierre del archivo | Closing the file |
|---|---|
|
|
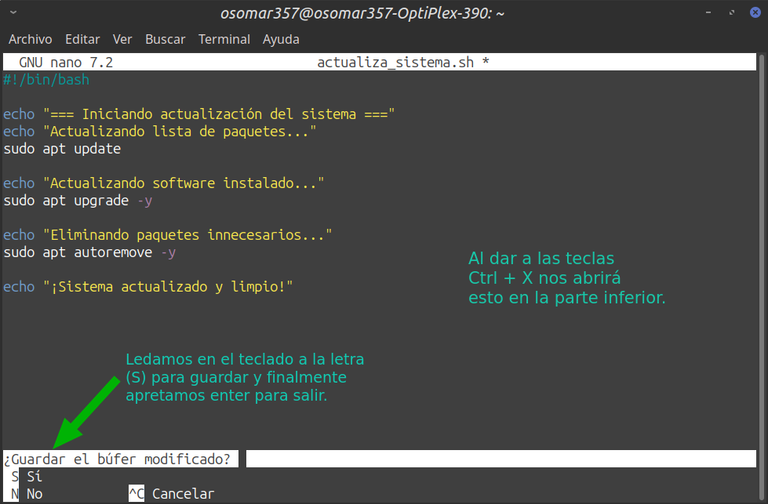
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Permisos de ejecución | Execution permits |
|---|---|
|
|
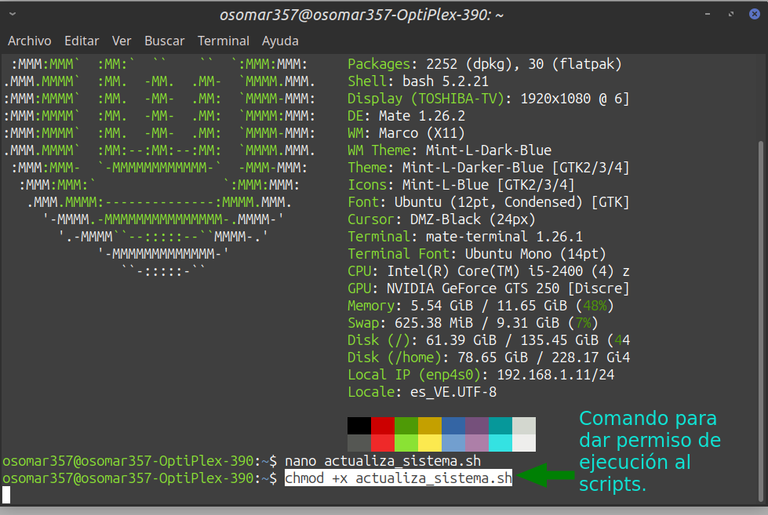
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Probando el script | Testing the script |
|---|---|
|
|

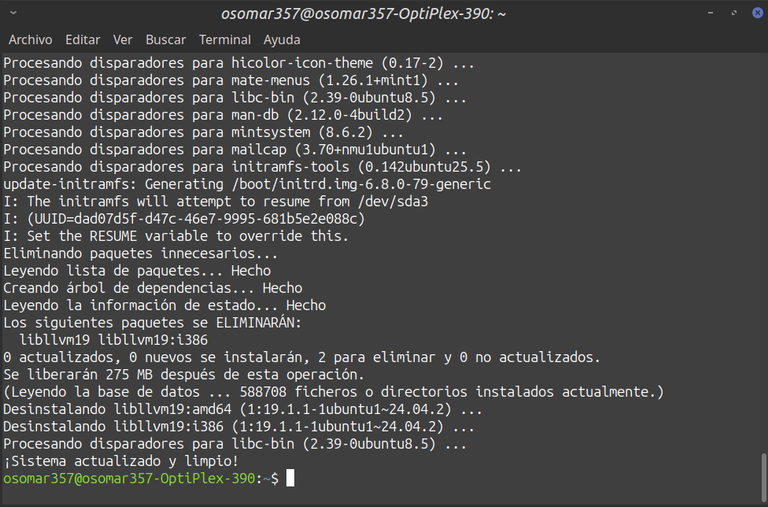
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Automatizar el script | Automating the script |
|---|---|
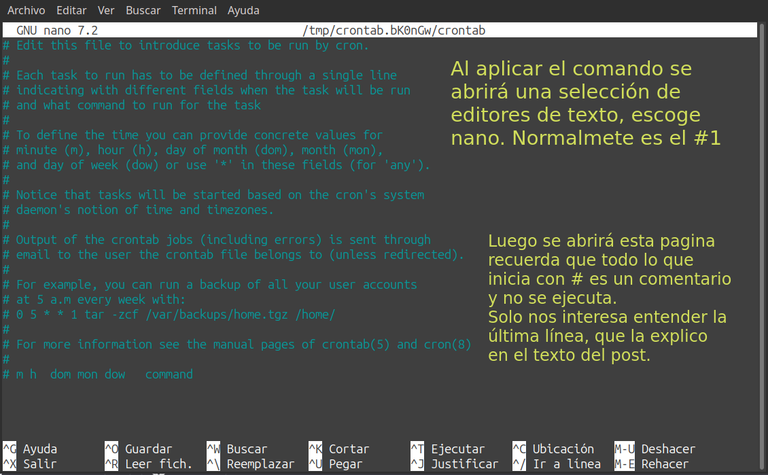
En mi caso, lo voy a colocar para que se ejecute de manera automática todos los días lunes a las dos de la tarde. Vamos con un paso a paso explicado a detalle. a) Abrimos una terminal y colocamos el comando: crontab -e Este comando abre el planificador de tareas. Ver la imagen. Esta última línea nos interesa ya que es el formato que usaremos: m h dom mon dow command Significa lo siguiente: m = minutos (de 0 a 59) h = hora (militar desde 1 a la 24) dom = día del mes (cubre del 1 al 31) mon = mes (cubre del 1 al 12) dow= día de la semana (cubre del 1 al 7. El 1 es el día lunes el 7 el domingo) command = comando a ejecutar. Creamos la línea de comando. m = 0 (significa cero minutos). h = 14 (significa 2 de la tarde). dom = (significa cualquier día) mom = (significa cualquier mes) dow = 1 (significa día lunes) command= /home/osomar357/Scripts/actualiza_sistema.sh (significa que el comando debe ejecutar el script actualiza_sistema.sh, que está en la carpeta /home del usuario: osomar357). La línea de comando completa quedaría así: 0 14 * * 1 /home/osomar357/Scripts/actualiza_sistema.sh |
In my case, I'm going to set it to run automatically every Monday at two in the afternoon. Let's go with a step by step explained in detail. a) Open a terminal and place the command: crontab -e This command opens the task planner. See the image. This last line interests us because it is the format we will use: m h dom mon dow command It means the following: m = minutes (from 0 to 59) h = time (military from 1st to 24th) sun = day of the month (covers 1st to 31st) mon = month (covers 1 to 12) dow = day of the week (covers 1 to 7. The 1st is the day Monday the 7th on Sunday) command = command to execute. We create the command line. m = 0 (means zero minutes). h = 14 (it means 2 in the afternoon). dom = (means any day) mom = (means any month) dow = 1 (it means Monday day) command= /home/osomar357/Scripts/actualiza_sistema.sh (it means that the command must execute the script actualiza_sistema.sh , which is in the user's /home folder: osomar357). The complete command line would look like this: 0 14 * * 1 /home/osomar357/Scripts/actualiza_sistema.sh |

Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Cerramos el planificador de tareas. | We closed the task planner. |
|---|---|
|
|

Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Verificar que se guardo el script | Verify that the script is saved |
|---|---|
|
|

Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Prueba de la automatización del script | Testing the automation of the scrip |
|---|---|
a) Abrimos de nuevo el editor de tareas con el comando: crontab -e. b) Agregamos esta línea al final: * * * * * echo "Cron funcionando: $(date)" >> /home/osomar357/cron-test.log c) Guardamos presionando las teclas: Ctrl + X para cerrar, la letra (S) para guardar y la tecla “Enter” para salir. d) Esperamos unos 3 minutos, y en la terminal colocamos este comando: cat /home/osomar357/cron-test.log Deberías ver un mensaje como este, ya que se está actualizando como prueba de manera constante: Cron funcionando: vie 05 sep 2025 15:31:01 -04 Cron funcionando: vie 05 sep 2025 15:32:01 -04 e) Ve a la terminal, elimina la última línea que pusiste para probar y guardamos de nuevo el archivo dando a las teclas: Ctrl + X para cerrar, la letra (S) para guardar y la tecla “Enter” para salir. | a) We open the task editor again with the command: crontab -e. b) We add this line at the end: * * * * * echo "Cron working: $(date)" >> /home/osomar357/cron-test.log c) We save by pressing the keys: Ctrl + X to close, the letter (S) to save and the “Enter” key to exit. d) We waited for about 3 minutes, and in the terminal we placed this command: cat/home/osomar357/cron-test.log You should see a message like this, as it is being updated as a test constantly: Cron working: fri 05 Sep 2025 15:31:01 -04 Cron working: Fri 05 Sep 2025 15:32:01 -04 e) Go to the terminal, delete the last line you put in to test and save the file again by giving the keys: Ctrl + X to close, the letter (S) to save and the “Enter” key to exit. |
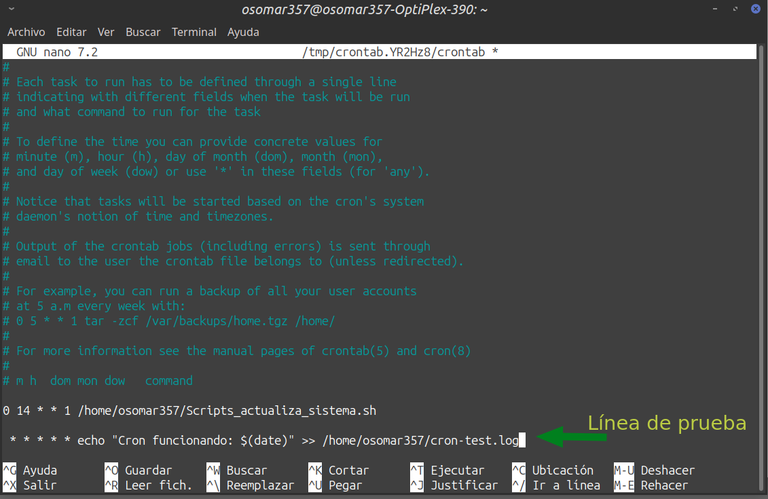

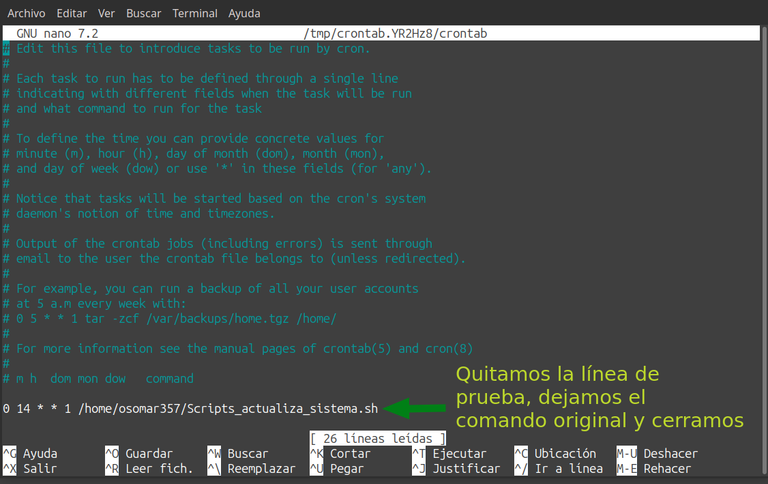
Captura de pantalla. / Screenshot.
Despedida | Farewell |
|---|---|
Espero que esta información haya sido de importancia para todos; les dejo un enlace donde hay un curso gratuito de Bash. Para la semana que viene intentaré hacer un script de limpieza del sistema y de la caché y dejarlo para que se realice de manera automática. Muchas gracias por leer mi post, mis mejores deseos para todos. | I hope this information has been of importance to everyone; I leave you a link where there is a free Bash course. For next week I will try to make a system and cache cleaning script and leave it to be done automatically. Thank you very much for reading my post, best wishes to all. |
Referencias:
Translated with www.yandex.com

Crece en Hive con el apoyo de Crypto Company.

#Archon, es una comunidad que apoya proyectos, resuelve problemas, y te ayuda a crecer en Hive.
Visita su Discord, tienen un chat en español.





[@PowerPaul:]
Hey! Because of your participation in the @CryptoCompany community and your participation in the "Banner for Boost" campaign you received a vote from your CryptoCompany and its trail! Thank you & Hive a great day!
Recent posting from @PowerPaul or the CryptoCompany network:
by @powerpaul
by @powerpaul
by @yourfairy
!discovery 30
!PIZZA
🐧😀👍💻
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@jlinaresp(4/15) tipped @osomar357
Come get MOONed!
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Consider setting @stemsocial as a beneficiary of this post's rewards if you would like to support the community and contribute to its mission of promoting science and education on Hive.
¡Enhorabuena!
✅ Has hecho un buen trabajo, por lo cual tu publicación ha sido valorada y ha recibido el apoyo de parte de CHESS BROTHERS ♔ 💪
♟ Te invitamos a usar nuestra etiqueta #chessbrothers y a que aprendas más sobre nosotros.
♟♟ También puedes contactarnos en nuestro servidor de Discord y promocionar allí tus publicaciones.
♟♟♟ Considera unirte a nuestro trail de curación para que trabajemos en equipo y recibas recompensas automáticamente.
♞♟ Echa un vistazo a nuestra cuenta @chessbrotherspro para que te informes sobre el proceso de curación llevado a diario por nuestro equipo.
🏅 Si quieres obtener ganancias con tu delegacion de HP y apoyar a nuestro proyecto, te invitamos a unirte al plan Master Investor. Aquí puedes aprender cómo hacerlo.
Cordialmente
El equipo de CHESS BROTHERS
@osomar357, I'm refunding 0.335 HIVE and 0.069 HBD, because there are no comments to reward.